Platforms: Cryosat-2
From
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| - | {| | + | <!--{| |
|[[File:HowTo.gif|thumb]] | |[[File:HowTo.gif|thumb]] | ||
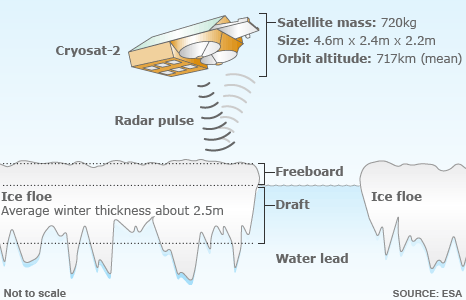
| Cryosat's radar has the resolution to see the Arctic's floes and leads<br>Some 7/8ths of the ice tends to sit below the waterline - the draft<br>The aim is to measure the freeboard - the ice part above the waterline<br>Knowing this 1/8th figure allows Cryosat to work out sea ice thickness | | Cryosat's radar has the resolution to see the Arctic's floes and leads<br>Some 7/8ths of the ice tends to sit below the waterline - the draft<br>The aim is to measure the freeboard - the ice part above the waterline<br>Knowing this 1/8th figure allows Cryosat to work out sea ice thickness | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|[[File:GravityField.jpg]] | |[[File:GravityField.jpg]] | ||
| CryoSat’s radar altimeter can sense the gravity field at the ocean surface,<br>so that seafloor characteristics at scales of 5–10 km are revealed.<br>This is the first altimeter in 15 years to map the global marine gravity field at such a high spatial resolution. | | CryoSat’s radar altimeter can sense the gravity field at the ocean surface,<br>so that seafloor characteristics at scales of 5–10 km are revealed.<br>This is the first altimeter in 15 years to map the global marine gravity field at such a high spatial resolution. | ||
| - | |} | + | |}--> |
<br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 3 December 2012
Спутник CryoSat-2 был запущен 9 апреля 2010 года с космодрома Байконур при помощи ракеты-носителя "Днепр-1". Искусственный спутник Земли Европейского космического агентства (ЕКА), предназначенный для измерения толщины и площади ледового покрова Антарктиды, Гренландии, Исландии, высокоширотных океанских зон, а также горных ледников при помощи высокоточного высотомера, способного работать в трех режимах. Спутник должен отслеживать динамику изменения ледников и прояснить вопрос о влиянии на них глобального потепления. Создан в рамках программы ЕКА «Живая планета». CrioSat-2 также предназначен для наблюдения за воздействием глобального потепления на полярные льды. Разработка спутника началась в 2002. 8 октября 2005 года спутник Криосат-1 был потерян в момент выведения из-за аварии ракеты «Рокот». 26 февраля 2006 ЕКА объявила, что спутник будет создан заново.
Спутник
dff
Результат
* Cryosat's radar has the resolution to see the Arctic's floes and leads
|
|
| This is the first altimeter in 15 years to map the global marine gravity field at such a high spatial resolution.
ИсточникиОписание: http://www.wikipedia.org/wiki/Криосат-2, http://www.ria.ru/science/20120528/659355789.html Изображения: ESA / AOES Medialab, http://www.esa.int, http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-12025283 |